In a landmark decision, Spokane, Washington, has become the first city in the US to prohibit crypto ATMs. The City Council cited a rise in scams targeting vulnerable populations as well as money laundering activities as reasons.
This move by the Spokane City Council has ignited a fierce debate: will such bans hinder crypto growth or foster a safer digital currency environment?
As Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies gain mainstream acceptance, local rulings like Spokane’s may have far-reaching consequences. This could potentially influence regulatory approaches nationwide and beyond.
In this article, we examine the impact of this ban on the future of crypto ATMs and the delicate balance between innovation and consumer protection.
United States’ Crypto ATMs Market
The United States dominates the crypto ATM market, hosting the vast majority of these machines worldwide. According to Coin ATM Radar, as of June 18, 2025, the U.S. boasts 30,256 crypto ATMs, accounting for more than 75% of the global total.

These kiosks, scattered across cities like Los Angeles, Miami, and New York, allow users to convert cash into cryptocurrencies or vice versa, offering a convenient entry point for those without access to traditional banking or online exchanges.
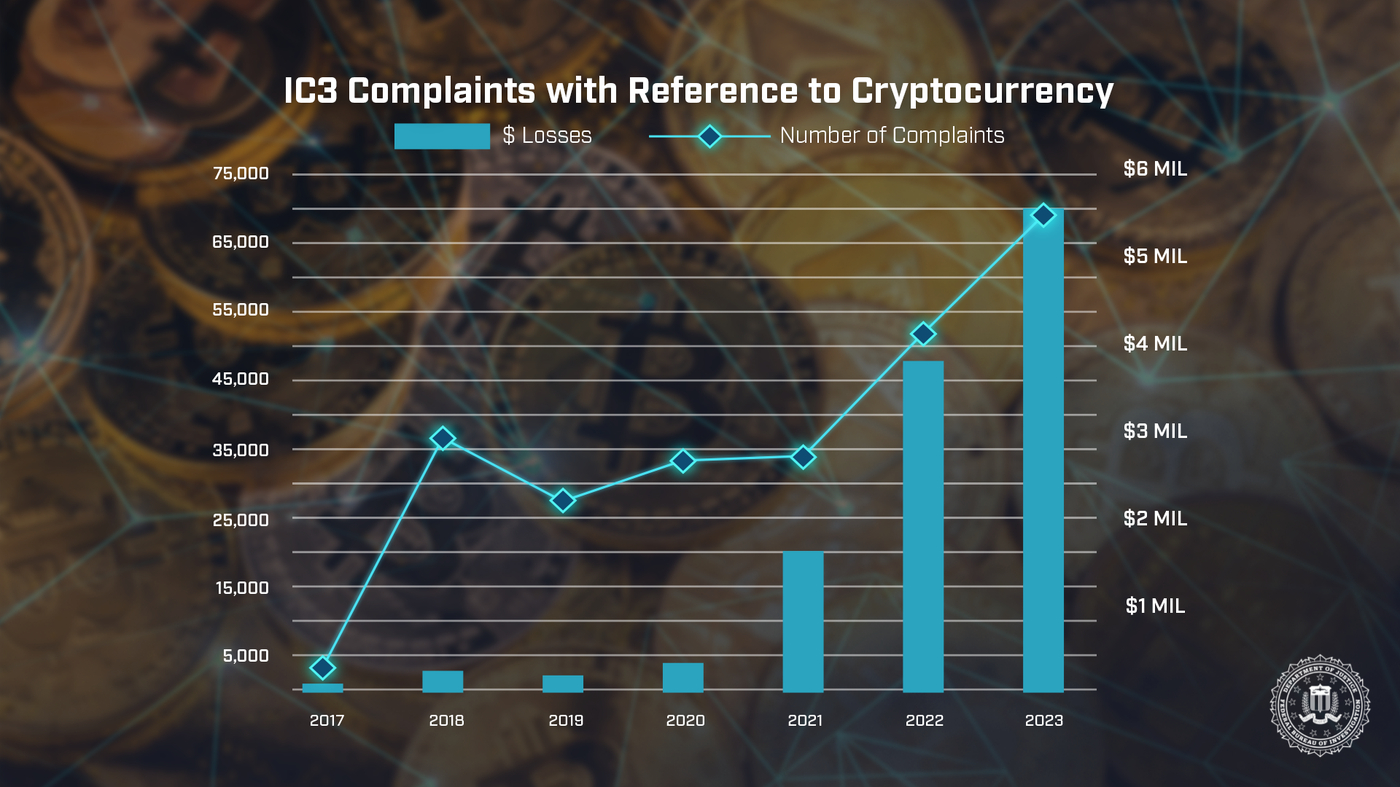
However, their accessibility has also made them a magnet for scammers, prompting regulatory scrutiny. Spokane’s ban, which mandates the removal of dozens of machines within 60 days, reflects growing concerns about fraud. The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) reported $5.6 billion in kiosk-related scam losses in 2023, including $142 million from Washington State alone.
How Many Crypto ATMs Are Present Across the Globe?
Globally, the crypto ATM network has seen remarkable growth, though recent data suggests a slight decline.
As of June 2025, approximately 39,000 crypto ATMs operate worldwide. The U.S. and Canada together account for about 90% of these kiosks, with Canada hosting 3,610 and Australia trailing at 1,850.
Other countries, like Germany with over 150 ATMs, also contribute to the global tally, but none rival the U.S. in scale. This widespread presence underscores crypto’s growing accessibility, particularly for unbanked populations or those seeking quick cash-to-crypto transactions.
Yet, the global landscape is uneven, with countries like China banning crypto ATMs outright. Australia has also imposed strict regulations to curb fraud.
Will Crypto Regulation Reduce the Number of Crypto ATMs Across the US and the World at Large?
Spokane’s ban signals a broader trend toward stricter crypto ATM regulations, which could significantly reduce their numbers both in the U.S. and globally.
In the U.S., states like Minnesota, California, and Vermont have already imposed transaction limits or licensing requirements. Aside from this, a proposed federal Crypto ATM Fraud Prevention Act aims to cap daily transactions for new users at $2,000 and mandate fraud warnings.
Such measures, while designed to protect consumers, may discourage operators due to compliance costs and reduced profitability.
For instance, Germany’s recent seizure of 13 unlicensed ATMs and the UK’s 90% reduction in active machines after a 2023 crackdown illustrate how enforcement can shrink ATM networks.
Globally, regulatory approaches vary widely. Brazil and Argentina are tightening rules to balance adoption and risk, while Singapore and China have outright bans.
These restrictions often target money laundering and fraud, as crypto ATMs’ anonymity makes them vulnerable to illicit use.
The Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK, for example, declared all unregistered crypto ATMs illegal, effectively halting their operation.
As regulators worldwide adopt similar measures, the global ATM count could decline further. This could hold true, especially in regions with stringent anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) requirements.
Impact on Crypto Usage and Adoption
Will Spokane’s ban and similar regulations stifle crypto usage and adoption? The answer is complex.
On one hand, crypto ATMs play a critical role in financial inclusion, offering unbanked individuals a gateway to digital currencies. Their removal could limit access for those who rely on cash transactions, potentially slowing adoption in underserved communities.
Latin America and Africa, for instance, have seen high crypto adoption for remittances and inflation protection, partly due to ATM availability. A reduction in kiosks might hinder these regions’ progress.
Conversely, enhanced regulation could bolster long-term adoption by fostering trust. Scams, which cost victims $65 million via crypto ATMs in the first half of 2024, erode confidence in cryptocurrencies.
By curbing fraud, regulations may make crypto a safer investment, attracting more mainstream users. The EU’s Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) framework, for example, balances consumer protection with innovation, potentially serving as a model for the U.S.
Moreover, regulatory clarity could encourage institutional adoption, as seen with the SEC’s approval of Bitcoin and Ethereum ETFs in 2024.

What does the future hold for crypto ATM?
Spokane’s crypto ATM ban highlights a pivotal moment for the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
While the immediate impact may reduce ATM availability, the long-term effects hinge on how regulators balance innovation and security.
Stricter rules could streamline the industry, weeding out bad actors and fostering a more trustworthy environment.
However, overly restrictive policies risk alienating users who depend on ATMs for access.
As the U.S. and other nations refine their regulatory frameworks, the crypto community must advocate for policies that protect consumers without stifling growth.
Ultimately, Spokane’s decision may be a precursor to a more regulated, yet potentially more robust, crypto landscape. Hopefully, the regulations will prioritise safety while preserving the promise of decentralised finance (DeFi).

